The key point of quality control of wire harness IPC620

The key point of quality control of wire harness IPC620 Contact us to get IPC620 english version printed book I. Processes Involved in Wire Harness Manufacturing The processes involved in wire harness manufacturing include but are not limited to: Cutting: Refers to cutting electronic wires or cables to the required length using machines or manually, without damaging the insulation or outer sheath. Outer Sheath Stripping: The outer sheath usually refers to the cable sheath. The outer sheath stripping machine should not scratch or cut the insulation of the core wires when stripping the outer sheath. Any cuts, breaks, cracks or splits in insulation (not shown). u Insulation thickness is reduced by more than 20% . u Uneven or ragged pieces of insulation (frays, tails, and tags) are greater than 50% of the insulation outside diameter or 1 mm [0.039 in] whichever is more . u Insulation is charred . u Insulation is melted into the wire strands . Core Wire Stripping: Adjust the core wire stripping machine to the required size for stripping, and be careful not to scratch or cut the copper wires. Crimping: Select the appropriate blade according to the terminal size. Crimp the prepared wire with the terminal crimp part using the blade, ensuring a firm crimp and that the appearance and pull force of the crimped terminal meet the standards. Put on connector: Insert the qualified crimped terminal wires into the matching connector housing. A clear click sound will be heard when the connector is fully inserted. Wire Twisting: Adjust the wire twisting machine to the appropriate height to ensure that the copper wires are not flattened or tangled, and the twisted conductor is in a uniform spiral shape. Tinning: Apply flux to the prepared...
Read More »How We Build Wire Harness Drawings ?
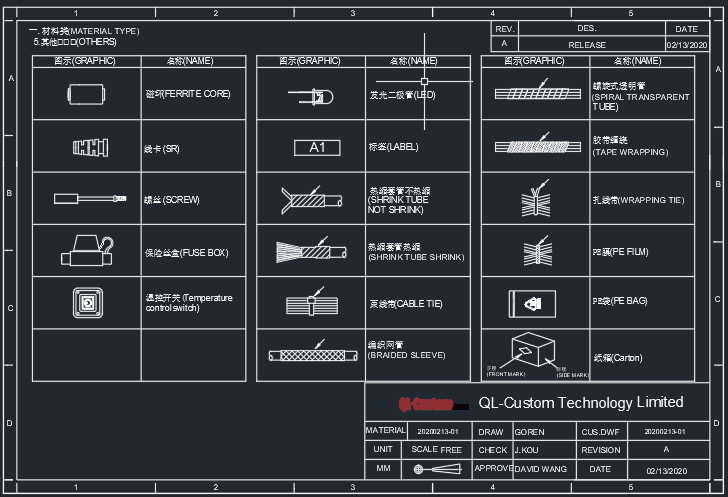
Overview of the Necessity and Importance of Wiring Harness Drawings Build wire harness drawings are essential for providing a clear and detailed representation of the harness layout, connection relationships, and component information. These drawings ensure the accuracy, reliability, and safety of the wiring harness. They illustrate the harness routing, including starting points, endpoints, and intermediate connection points, as well as the harness path. Moreover, the drawings depict the connection methods and relationships of each wire within the harness. As the primary source of information for wiring harness production, these drawings play a fundamental and critical role in the manufacturing process. Wire harness drawings build from customers' drawings : QL-Custom's Process from Inquiry Receipt to Drawing Submission for Customer Review : Upon receiving an inquiry, including customer drawings or samples, our engineers determine the sourcing strategy, whether it's original or domestic materials. They then source quotes from multiple suppliers, comparing prices to offer the best option to the customer. After price confirmation, a sample request is submitted. Engineers create drawings based on customer-provided information or samples. After internal review and approval, the drawings are sent to the customer for confirmation. Drawing Considerations and Details – Analyze customers' drawing to generate our Drawing : [caption id="attachment_4230" align="alignnone" width="796"] Wire Harness Drawings[/caption] As shown above, a typical drawing consists of seven main sections: Drawing information: Customer part number, internal part number, drafter, reviewer, revision level, date, etc. Revision history: Details of any changes made to the drawing. Quality and testing requirements: Specific standards and tests the harness must meet. 2D layout: A comprehensive view showing component placement, wire lengths, and other crucial manufacturing details. Circuit diagram: Illustrates the point-to-point connections within the harness. Bill of Materials (BOM): Lists all components, including wires, terminals, connectors, and sleeving, with quantities and internal part...
Read More »